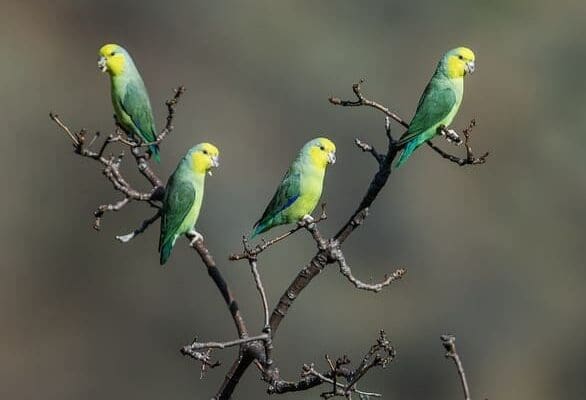
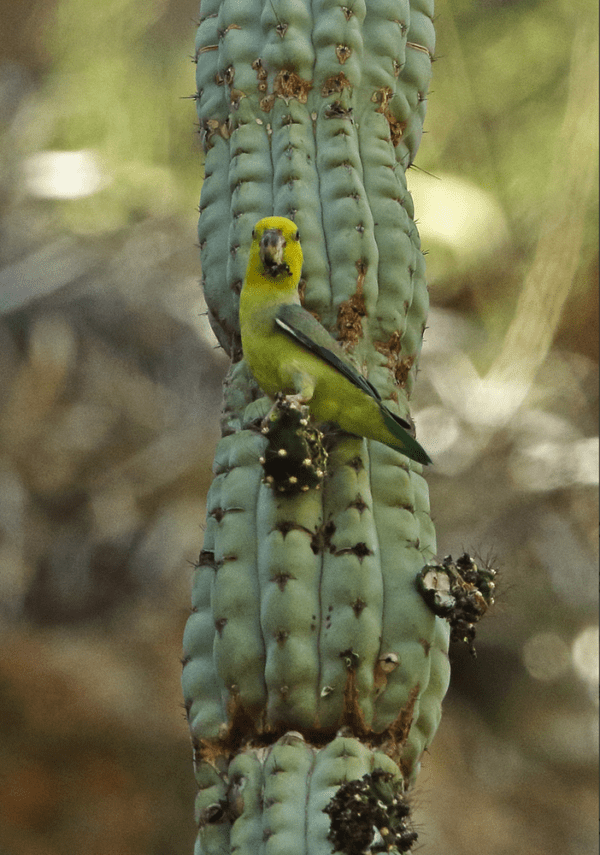
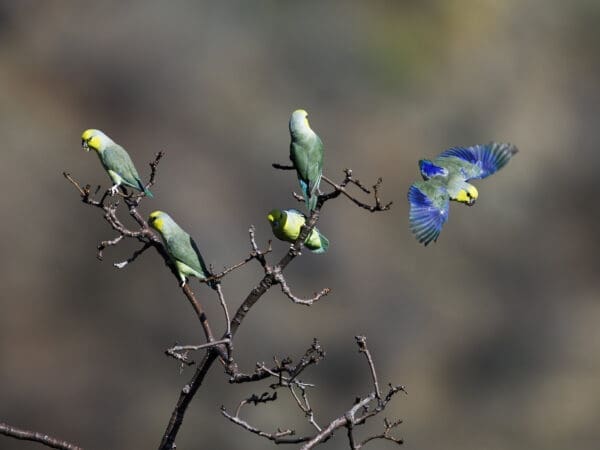
![© Nick Athanas [CC BY 2.0] via Flickr Wild Yellow-faced Parrotlets perch in a bare tree](https://parrots.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/wpt_Yellow-faced-Parrotlet_1371-7-e1731089683144-100x100.jpg)
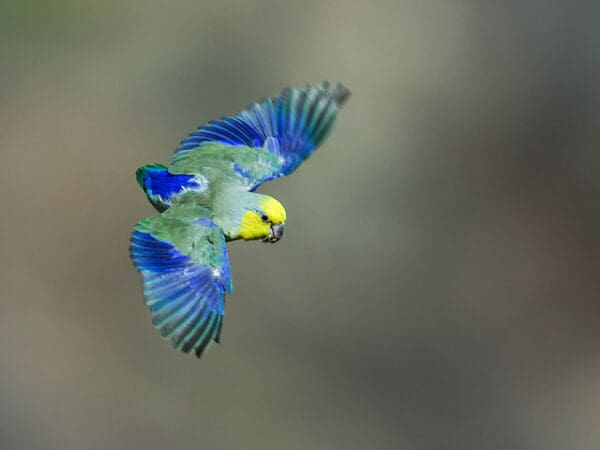
![© Nick Athanas [CC BY 2.0] via Flickr A wild Yellow-faced Parrotlet glides](https://parrots.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/wpt_Yellow-faced-Parrotlet_1371-6-100x100.jpg)
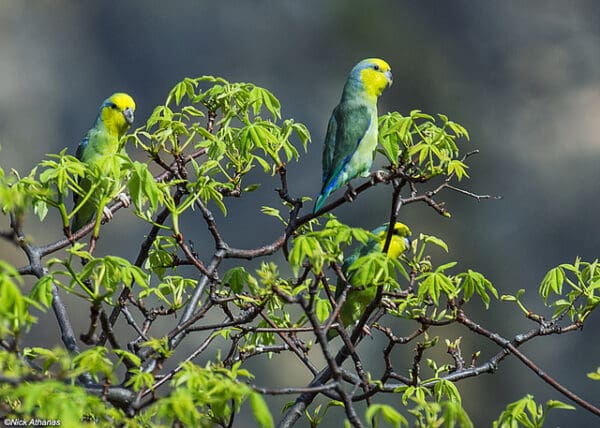
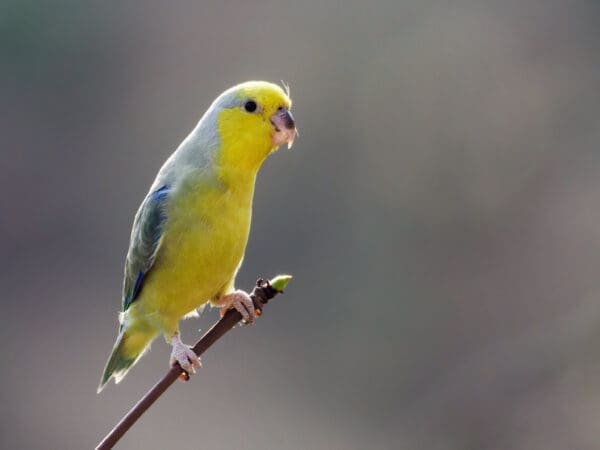
![© Nick Athanas [CC BY 2.0] via Flickr Wild Yellow-faced Parrotlets perch in a leafy tree](https://parrots.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/wpt_Yellow-faced-Parrotlet_1371-5-100x100.jpg)
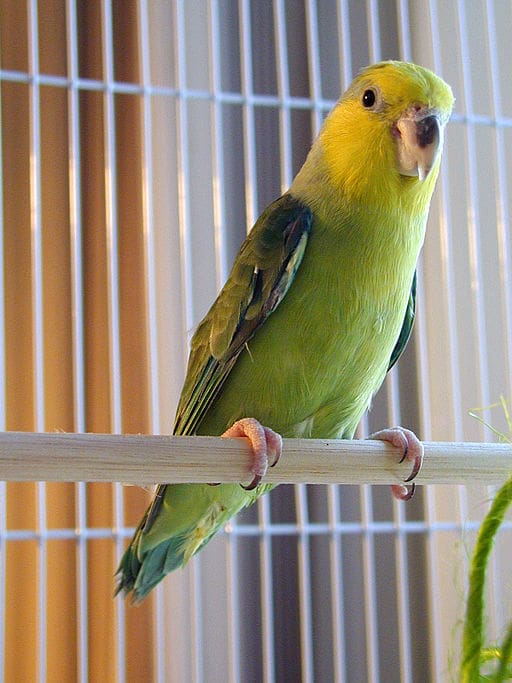
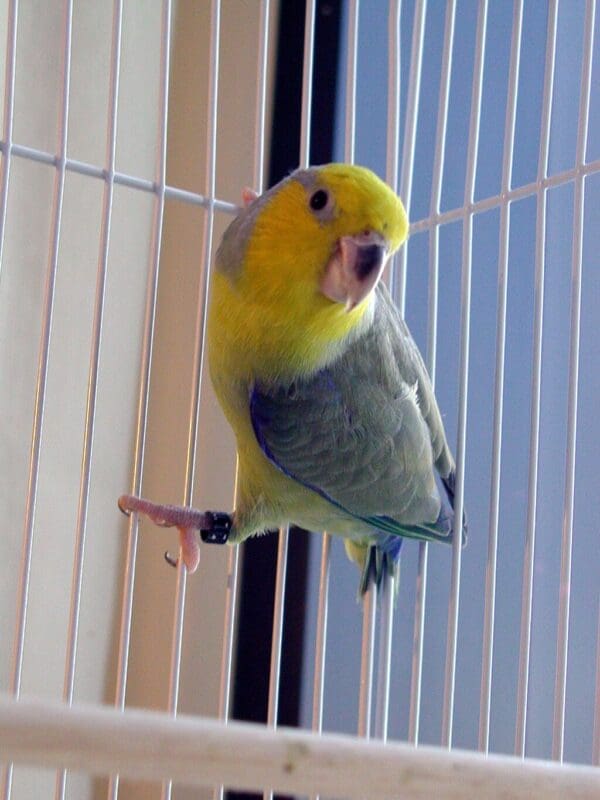
![© Ruth Rogers [CC BY 2.0] via Wikimedia Commons A companion Yellow-faced Parrotlet perches on dowel](https://parrots.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/wpt_Yellow-faced-Parrotlet_1371-2-100x100.jpg)






DID YOU KNOW?
Parrotlets were kept in France as long ago as 1682.

Forpus

xanthops
Size:
14.5 cm (5.6 in)
Weight:
35 g (1.2 oz)
Subspecies including nominate:
one
Colour Adult:
Male-bright yellow forehead, crown, cheeks and throat; occiput and nape purple/grey, extending in a stripe to eye; olive/grey mantle, upper back and lesser wing coverts to scapulars and inner secondary feathers; deep blue lower back, rump, upper tail coverts and underwing coverts; purple/blue secondary coverts; inner primary feathers suffused with blue at bases; green/yellow underparts. Beak horn in colour with grey at base of upper mandible. Eye brown. Female-as in male but lower back and rump paler blue; primary and secondary coverts, secondary feathers and bases to primary feathers all green tinged with blue.
Colour Juvenile:
As in adults but dull overall, less yellow on face. Grey absent on beak.
More Information:
Content Sources:
CITES
BirdLife International
Cornell Lab of Ornithology/Birds of the World
Parrots: A Guide to the Parrots of the World, Juniper and Parr, 1998
Parrots: Status Survey and Conservation Plan 2000-2004, Snyder, McGowan, Gilardi and Grajal, 2000.
Parrots of the World, Forshaw, 2006. 2010 edition
Parrots in Aviculture, Low, 1992.
Lexicon of Parrots, Thomas Arndt.
Psittacine Aviculture, Schubot, Clubb and Clubb, 1992.
Parrots: Their Care and Breeding, Low, 1986.
Captive Status:
Rare; unknown until 1979 or so.
Longevity:
15-25 yrs.
Housing:
Walk-in enclosure, minimum length 2.1 m (7 ft) or indoor aviary minimum length 1.8 m (6 ft).
Diet:
Small seed mix: canary, millet and smaller amounts of oats, buckwheat and safflower; limited sunflower seed; spray millet; seeding grasses; green leaves such as: Swiss chard, lettuce, dandelion, chickweed, sowthistle; rearing food made with hard-cooked eggs, carrot and wholegrain bread all ground up; fruits such as: apple, pear, etc; complete kibble.
Enrichment:
Bathing using overhead misters or shallow water bowls, socialization; swings, ladders, perches, chew items (fir, pine, willow twigs, sterilized pine cones, vegetable tanned leather), foraging toys, puzzle toys.
Nest Box Size:
6″ x 6″ x 6″ (15.2 cm x 15.2 cm 15.2 cm) vertical box
Clutch Size:
3 to 6
Fledging Age:
5-6 weeks
Hatch Weight:
—
Peak Weight:
—
Weaning Weight:
—
World Population:
250-1000 mature individuals, stable.
IUCN Red List Status:
Vulnerable
CITES Listing:
Appendix II
Threat Summary:
In the past, this species has undergone rapid population reductions owing to exploitation for the cage-bird trade, where the mortality rate during capture is estimated at 40-100%. A ban on trade in Peru was introduced, reducing the number trapped. If pressure from the cage-bird trade were to increase and the population declined again, its status would revert from Vulnerable to Endangered. An emerging threat is the construction of four dams on the Rio Marañón.
Range:
NW Peru; confined to upper Rio Marañón valley, from E La Libertad north to SE Cajamarca and S Amazonas.
Habitat:
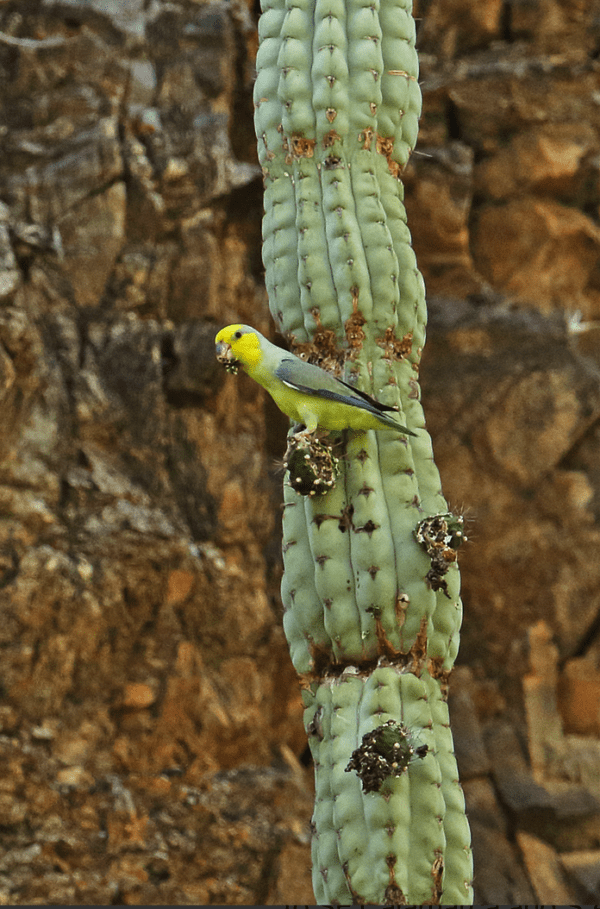
Found from 800-1000 m (2624-3280 ft), rarely 2400 m (7872 ft), in arid, lightly wooded habitats in the upper tropical and subtropical areas including scrub, riparian vegetation, open balsa woodland, cactus montane desert and open country with scattered vegetation.
Wild Diet:
Food items include cactus and tree fruits, seeds of Cercidium praecox and flowers including Bombax discolor; also forages on the ground for grass and wheat seeds.
Ecology and Behaviour:
Social birds; roosts communally. Up to 70 pairs in communal nesting area.
Clutch and Egg Size:
3 to 6 eggs.
Breeding Season:
March-April; nests reportedly seen in natural dirt and rock walls in colonies of up to 70 birds. Old woodpecker cavities are also used.
Related Links:
—